What is Radon ?

Radon is a radioactive gas that has been found in homes all over the Unites States. It comes from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock and water and gets into the air you breathe. Radon typically moves up through the ground to the air above and into your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Radon can also enter your home through well water. Your home can trap radon inside.
Any home can have a radon problem. This means new and old homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, and homes with or without basements. In fact, you and your family are most likely to get your greatest radiation exposure at home. That is where you spend most of your time.
My Home Has Radon-Resistant Features and I Had it Tested
Since I am always advising my clients about Radon and that they should do a Radon test, I decided to take my own advice.
My home is 2 1/2 years old and was built by a well-known builder in the area. One of the quality of construction features installed in the home is "Radon-Resistant Features (Techniques)". I was curious to know if that actually makes a difference?
I called Ryan Goodsell, of Circle G Inspections to perform the test. Ryan uses the "Active Device" for testing and it was continuous monitoring from Friday evening to Monday evening. The test results came in at an average of 1.1 pCi/L. Ryan said it was the lowest level he has ever seen in a home that did not have a Radon Mitigation system installed. A Radon Mitigation system is installed when a home has high levels (over 4.0) of Radon. The test results confirm that I made a good choice when selecting my new home!
ABOUT RADON LEVELS
Radon In Mesa County
The average indoor radon levels of Mesa County, as determined by radon test results from Air Chek, Inc, is 4.6 pCi/L
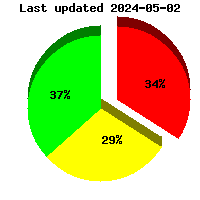 |
Results under 2 pCi/L
Results between 2 and 3.9 pCi/L Results 4 pCi/L and above |
Radon Resources
What Are Radon-Resistant Features?
Radon-resistant techniques (features) may vary for different foundations and site requirements. If you are having a home built, ask your builder if they are using a recognized approach (International Residential Code, Appendix F, ASTM E 1465-08, and ANSI/A/AARST RRNC 2.0 as examples. If your new house was built (or will be built) to radon-resistant, it will include these basic elements:
- Gas-Permeable Layer: This layer is placed beneath the s lab or flooring system to allow the soil gas to move freely underneath the house. This gas-permeable layer is used only in homes with basement and slab-on-grade foundations, it is not used in homes with crawlspace foundations.
- Plastic Sheeting: Plastic sheeting is placed on top of the gas-permeable layer and under the slab to help prevent the soil gas from entering the home. In crawl spaces, the sheeting (with all seams sealed) is placed directly over the crawl space floor.
- Sealing and Caulking: All below-grade openings in the foundation and walls are sealed to reduce soil gas entry into the home.
- Vent Pipe: a 3- or 4-inch PVC pipe (or other gas-tight pipe) runs from the gas-permeable layer through the house to the roof, to safely vent radon and other soil gases to the outside.
- Junction Boxes: An electrical junction box is installed in case an electric venting fan is needed later.


